Introduction to glycine and why it matters
Glycine is one of those tiny things in the body that does a very big job. It is an amino acid, which means it helps build proteins. But glycine is not only about muscles or fitness. It works quietly in many parts of the body every single day. From helping you sleep better to supporting your brain, skin, and digestion, glycine is always active behind the scenes. Many people have heard the name but do not really know what it does. So let’s slow down, keep things simple, and explain it in a human way 😊
What exactly is glycine
Glycine is the smallest amino acid. Because it is small, it moves easily in the body and fits into many important processes. The body can make glycine on its own, which means it is called a “non-essential” amino acid. But here is the catch: sometimes the body does not make enough of it. Stress, poor diet, illness, or aging can increase the need for glycine. That is when food sources and smart nutrition become important.
How glycine helps build proteins
Proteins are like the building blocks of your body. Muscles, skin, hair, enzymes, and even hormones depend on proteins. Glycine plays a key role in making these proteins stable and strong.
It is especially important for collagen, which is the most abundant protein in the human body. Collagen keeps your skin firm, your joints flexible, and your bones strong. In fact, glycine makes up nearly one-third of collagen. Without enough glycine, collagen production can slow down.
So when people talk about healthy skin, joints, and anti-aging, glycine is quietly doing a lot of the work 💪
Role of glycine in collagen formation
Collagen is everywhere in your body. It supports your skin, tendons, ligaments, cartilage, and even blood vessels. Glycine gives collagen its flexible structure. Think of glycine as the glue that holds collagen fibers together.
When glycine levels are healthy:
- Skin looks smoother and more elastic
- Joints move more comfortably
- Wounds heal faster
- Bones stay stronger
This is one reason bone broth, which is rich in glycine, has been popular for centuries.
Glycine and brain function
Your brain uses chemical messengers called neurotransmitters to send signals. Glycine acts as one of these messengers. But unlike stimulants, glycine is calming.
It helps control nerve signals and prevents overactivity in the brain. This means glycine can:
- Support mental calmness
- Reduce nervous tension
- Help with focus and clarity
Glycine also works with another neurotransmitter called glutamate to support learning and memory. So it is not just about calmness; it is also about balance 🧠
How glycine supports better sleep
Many people struggle with sleep, even when they feel tired. Glycine helps by lowering body temperature slightly and calming brain activity before sleep.
Research has shown that glycine may:
- Help you fall asleep faster
- Improve sleep quality
- Reduce daytime sleepiness
The best part? Glycine does not act like a sleeping pill. It does not knock you out. Instead, it gently supports the body’s natural sleep rhythm. That is why some people feel more refreshed in the morning after improving their glycine intake 😴
Glycine and muscle repair
After physical activity, muscles need repair. Glycine helps build new muscle tissue and supports recovery. It also helps reduce muscle breakdown during stress or intense exercise.
For people who:
- Exercise regularly
- Do physical work
- Are recovering from illness
Glycine can be very helpful. It supports strength while also protecting muscle tissue.
Blood sugar control and glycine
Glycine plays a role in how the body handles sugar. It supports insulin function, which helps move sugar from the blood into the cells where it is used for energy.
Balanced glycine levels may:
- Help keep blood sugar stable
- Reduce sudden sugar spikes
- Support metabolic health
This does not mean glycine is a cure, but it does support the system that keeps blood sugar under control 🍽️
Glycine and digestive health
Your digestive system needs protection, especially the lining of the stomach and intestines. Glycine helps strengthen this lining and supports healthy digestion.
It may help:
- Reduce irritation in the gut
- Support nutrient absorption
- Protect against digestive stress
This is one reason traditional diets often included slow-cooked meats and broths. These foods naturally contain glycine and support gut health.
Liver detox support
The liver is your main detox organ. Glycine helps the liver remove harmful substances from the body. It supports a process called conjugation, where toxins are made safer and easier to remove.
When glycine is sufficient:
- The liver works more efficiently
- Oxidative stress is reduced
- Overall detox pathways stay balanced
This is especially important for people exposed to pollution, medications, or processed foods 🌿
Glycine and immune system balance
The immune system needs to be strong but not overactive. Glycine helps regulate inflammation and immune responses.
It may:
- Reduce excessive inflammation
- Support healthy immune signaling
- Protect tissues during immune reactions
This balanced approach is important because too much inflammation can be just as harmful as too little immunity.
Heart health and glycine
Glycine supports heart health in subtle ways. It helps relax blood vessels and supports healthy blood flow. This can reduce strain on the heart.
Some studies suggest glycine may:
- Support healthy blood pressure
- Reduce oxidative stress in blood vessels
- Improve overall cardiovascular balance ❤️
Again, it is not a medicine, but it is a supportive nutrient that works quietly in the background.
Glycine and mental stress
Stress affects the body in many ways. Glycine helps calm the nervous system and may reduce the physical impact of stress.
People often describe glycine as “grounding.” It does not make you sleepy during the day, but it helps smooth out stress responses. That calm feeling matters more than we often realize.
Natural food sources of glycine
Glycine is found mostly in protein-rich foods, especially those that include connective tissue.
Here is a simple table for easy understanding:
| Food Source | Glycine Content Level |
|---|---|
| Bone broth | Very High |
| Chicken skin | High |
| Beef (slow-cooked) | High |
| Fish skin | Moderate |
| Gelatin | Very High |
| Eggs | Moderate |
| Legumes | Low to Moderate |
Traditional diets naturally included more glycine-rich foods. Modern diets often focus only on muscle meat, which can create an imbalance.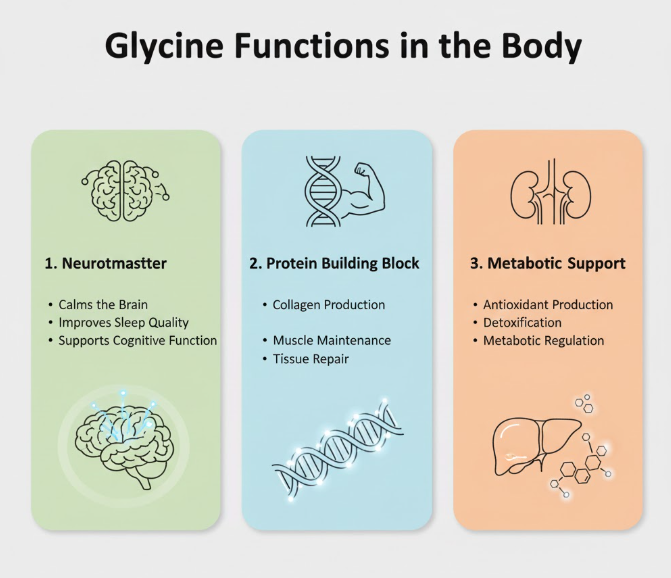
Glycine supplements: simple overview
Some people use glycine supplements, especially for sleep or joint support. Glycine powder is usually tasteless and easy to mix with water.
However, food sources should always come first. Supplements are helpful when diet alone is not enough. Always start slow and listen to your body.
Signs you may need more glycine
The body does not send clear messages, but some signs may include:
- Poor sleep quality
- Joint discomfort
- Slow wound healing
- High stress levels
- Digestive discomfort
These signs do not mean glycine deficiency for sure, but they can be clues worth paying attention to.
Is glycine safe
Glycine is generally very safe when consumed through food. It is already present in the body and used daily. Moderate supplemental amounts are usually well tolerated.
As with anything, balance matters. More is not always better.
Why glycine is often overlooked
Glycine does not have flashy marketing. It is not trendy like some supplements. But that does not reduce its importance. In fact, its quiet role is exactly why it matters so much.
Sometimes the most powerful nutrients are the simplest ones 🙂
Quick summary table of glycine functions
| Body Area | How Glycine Helps |
|---|---|
| Skin & Joints | Supports collagen strength |
| Brain | Calms nerves, supports focus |
| Sleep | Improves sleep quality |
| Muscles | Aids repair and recovery |
| Liver | Helps detox processes |
| Digestion | Protects gut lining |
| Heart | Supports healthy blood flow |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Is glycine the same as protein?
No. Glycine is one building block of protein. Proteins are made of many amino acids, and glycine is one of them.
Can I get enough glycine from food alone?
Yes, especially if you eat bone broth, slow-cooked meats, and whole animal foods. Many people can meet their needs through diet.
Does glycine help with anxiety?
Glycine supports calm brain signaling. It may help reduce nervous tension, but it is not a replacement for medical treatment.
Is glycine good for aging skin?
Yes. Because it supports collagen production, glycine plays a role in maintaining skin elasticity and structure.
Can glycine be taken daily?
From food, yes. For supplements, daily use is common, but moderation is important.
Final thoughts on glycine
Glycine is simple, small, and often ignored. But it supports the body in deep and meaningful ways. From better sleep to stronger joints and calmer nerves, glycine works quietly but consistently.
When nutrition focuses only on the latest trend, basic nutrients like glycine get forgotten. Bringing them back into daily life, through food and smart choices, can make a real difference over time 🌱